Understanding Ethereum Mining: How Blocks Are Confirmed and Added to the Blockchain
Ethereum’s decentralized and open-source nature has made it one of the most widely used blockchain platforms in the world. At its core, Ethereum is built on a consensus algorithm called proof-of-work (PoW), which requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to confirm transactions and create new blocks. In this article, we’ll dive deeper into the process of validating blocks in Ethereum mining.
Mining Process
Here’s an overview of the related actions:
- Transaction receipt: When a user sends cryptocurrency or data via an Ethereum wallet, it is broadcast to the network.
- Transaction confirmation: The transaction is verified by network nodes to ensure it is valid and complies with Ethereum’s rules.
- Block Creation: Once a sufficient number of transactions have been confirmed, the block creator (known as a “block miner”) selects a group of unconfirmed transactions called a “block” or “blockchain snapshot.”
- Hash Function: The block is mined using a complex mathematical algorithm, specifically SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256). This process involves calculating a unique fingerprint for each block.
- Block Validation
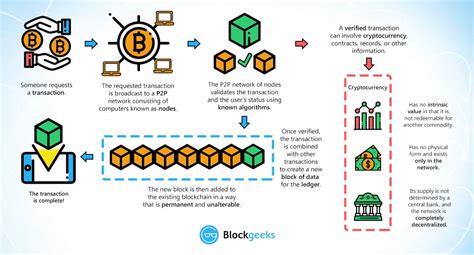
: Once a block hash is calculated, it must be verified by multiple network nodes to ensure that:
- The block has enough transactions (at least one “mining transaction”) and is not empty
- All transactions in the block are valid and comply with Ethereum’s rules
- The block hash is unique and consistent across the network
- Block Addition: If the block passes validation, it is added to the blockchain as a new block.
The Role of Hash Functions
SHA-256 (or similar) hash functions play a crucial role in block verification. By calculating a unique fingerprint for each block, miners can ensure that the block data has not been corrupted or altered during transmission. This ensures the integrity and authenticity of the transactions being verified.
Proof of Work: Mining Algorithm
The Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm is used to confirm transactions on the Ethereum network. Miners compete to solve a complex mathematical puzzle that requires significant computing power and energy expenditure. The miner who solves the puzzle must first add their transaction to the blockchain because they solved the most difficult puzzle.
Conclusion
In summary, block validation in Ethereum mining involves several basic steps:
- Transaction receipt
- Block creation (including hashing)
- Transaction verification
- Block content confirmation
- Block reload
A unique fingerprint calculated using SHA-256 ensures that each block is verified and included in the blockchain. The proof-of-work algorithm requires significant computing power, but it is a secure way to confirm transactions on the Ethereum network.
I hope this article helped you understand how blocks are confirmed in Ethereum mining!